
Unique Anatomies
Patient-Matched
Solutions
MySpine Anchor is Medacta’s Patient-Matched Solution for posterior Sacro-Iliac fusion: a solution for long constructs, designed to potentially overcome insufficient lower spine fixation.
The MySpine Anchor technique represents a solution to minimize instrumentation failure at the end of long constructs and reduce risk of screw loosening. This technique could provide additional stability and fusion in spinal deformities where there is a tendency of SI joint dysfunction[1].
The stabilizing effect of S2-Alar-Iliac screws in combination with posterior SI fusion devices may reduce the risk of mechanical failure of S1 pedicle screws[2]. Divergent S2-Alar-Iliac trajectories may support a smaller incision and less lateral retraction compared to S2-Alar trajectories[3].
MySpine Anchor is Medacta’s Patient-Matched Solution for posterior Sacro-Iliac fusion as an adjunct to thoracopelvic fixation.
This solution is designed to potentially overcome insufficient lower spine fixation in long spine constructs.
This guided technique leads to accurate screw positioning and potential reduction in radiation exposure and surgical time compared to free-hand technique[4,5].
The all-in-one guide performs S2AI and SI pilot hole preparation without increasing operation time compared to free-hand technique.

Low Dose CT scan creates 3D reconstructed vertebrae and the pelvic region

Optimal implant parameters are defined by the surgeon

Patient-matched Jigs are sent to the hospital

Support during first cases is provided by an experienced surgeon
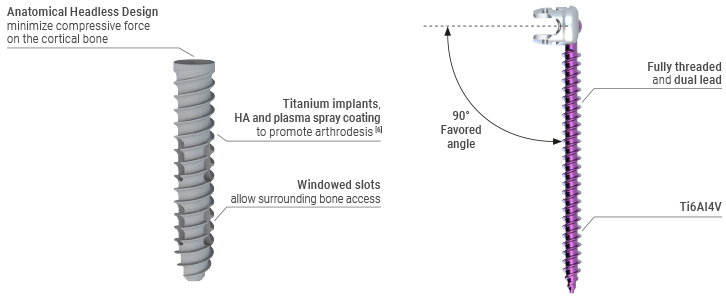
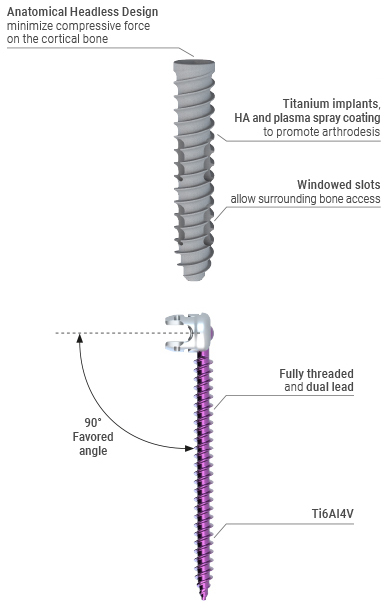
The MySpine Anchor patient specific drill guide is accompanied with by the M.U.S.T. Pedicle screw system, which has a unique low-profile screw head design and is available in 8.0, 9.0, and 10.0 mm screw sizes.
This technique also accompanies the M.U.S.T. Sacro-Iliac Headless Screw system, which has an anatomical headless design to minimize compressive force on the cortical bone and a hydroxyapatite rough plasma spray coating to promote fusion[6].
[1] Kebaish KM. Sacropelvic fixation: techniques and complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35(25): 2245–2251.
[2] Casaroli et al. “Evaluation of iliac screw, S2 alar‑iliac screw and laterally placed triangular titanium implants for sacropelvic fixation in combination with posterior lumbar instrumentation: a finite element study”. European Spine Journal (2019) 28:1724–1732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-019-06006-0.
[3] S.M.Krieg et al. “Revision by S2-alar-iliac instrumentation reduces caudal screw loosening while improving sacroiliac joint pain—a group comparison study”. Neurosurgical Review (2021) 44:2145–2151.
[4] Ai-Min Wu et al. “The technique of S2-alar-iliac screw fixation: a literature review”. http://amj.amegroups.com/article/view/4197/4924.
[5] Matsukawa K. et al., Cortical pedicle screw trajectory technique using 3D printed patient-specific-guide, M.O.R.E. Journal, September 2018.
[6] Strnad Z., Strnad J., HYPERLINK “https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ctibor-Povysil” Povýsil C., Effect of Plasma-Sprayed Hydroxyapatite Coating on the Osteoconductivity of Commercially Pure Titanium Implants. HYPERLINK “https://www.researchgate.net/journal/The-International-journal-of-oral-maxillofacial-implants-1942-4434” The International journal of oral & maxillofacial implants. July 2000; 15(4):483-90.